Table of contents
Open Table of contents
DynamoDB 101
Paper内容之前,先简单介绍一下 DynamoDB。
What is DynamoDB
- NoSQL, KV database
- Unlimited store and retrieve any amount of data and serve any level of request traffic
- TTL
- PartiQL or classic APIs to query
- 没有 predefined attributes order 的概念,可以随意插入(区别于 mysql)
- 本地开发可以使用 DynamoDB locally
- DynamoDB provides single-digit millisecond performance for workloads of all sizes
- Amazon DynamoDB stores data in partitions.
- A partition is an allocation of storage for a table, backed by solid state drives (SSDs) and automatically replicated across multiple Availability Zones within an AWS Region.
DynamoDB Core Components
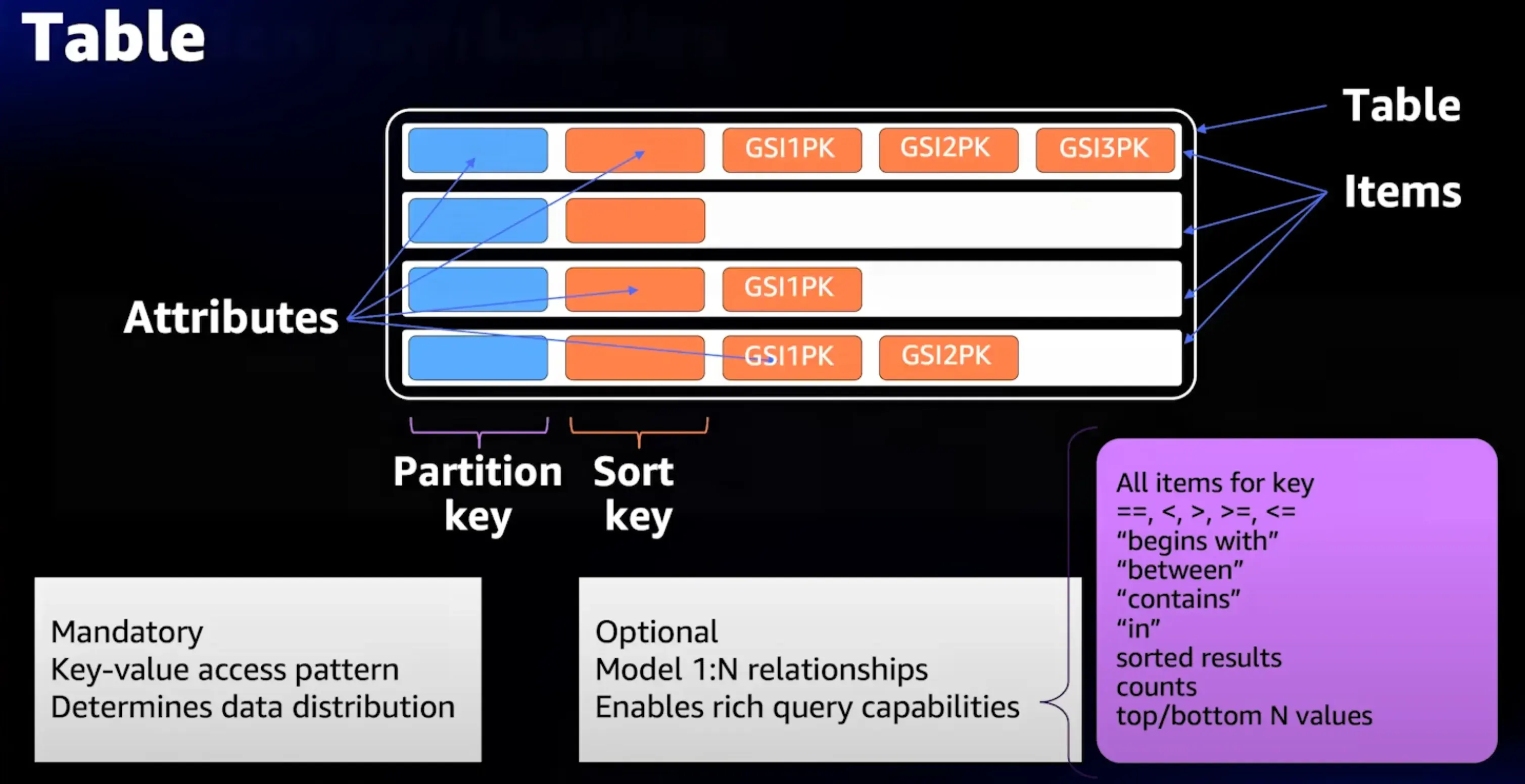
-
tables
- A table is a collection of data
-
items
- An item is a group of attributes that is uniquely identifiable among all of the other items.
-
attributes
- Primary key to uniquely identify each item
- Each item can have its own distinct attributes.
- Secondary indexes to provide more querying flexibility.
-
DynamoDB Streams to capture data modification events in DynamoDB tables.
Primary Key
Two types of different kinds:
- Partition key, composed of one attribute know as the partition key.
- hash(partition_key) determines the partition
- a table only one partition key
- PartitionKey(hash attribute) and sort key(range attribute), aka composite primary key.
- hash(partition_key) determines the partition
- stored in sorted order by sort key value.
Secondary Indexes
Two types of different kinds:
- Global secondary index – An index with a partition key and sort key that can be different from those on the table.
只支持 Eventually consistent reads
- Local secondary index – An index that has the same partition key as the table, but a different sort key.
Others
- Supported data types and naming rules in Amazon DynamoDB - Amazon DynamoDB
- DynamoDB examples using SDK for Go V2 - AWS SDK Code Examples
Introduction
Amazon DynamoDB 是一个非常重要的 NoSQL Database,它起源于 Amazon 的 Dynamo。
目前在 Amazon 和 AWS 内部广泛使用,而且很多的 AWS Services 也是用到了 DynamoDB, 比如 AWS Lambda。
DynamoDB 通过牺牲功能性来换取了 fast and predictable performance at any scale。
- DynamoDB is a fully managed cloud service
- DynamoDB employs a multi-tenant architecture
- DynamoDB achieves boundless scale for tables
- DynamoDB provides predictable performance (service-side latency in the low single-digit ms range for 1 KB item)
- DynamoDB is highly available
- DynamoDB supports flexible use cases
History
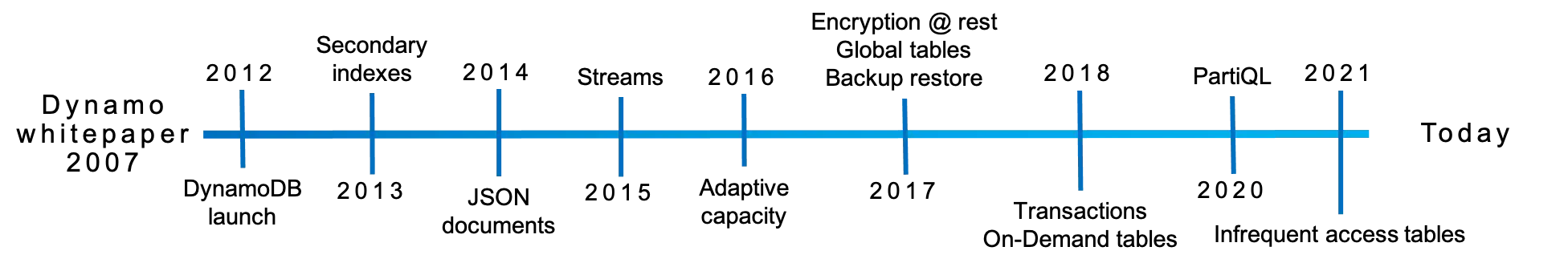
- 支持 SQL interface 已经成为了一种共识,还多 NoSQL 都添加了 SQL 的支持
- DynamoDB PartiQL (2020)
- Cassandra CQL
- Aerospike AQL
- Couchbase SQL++
- MongoDB added SQL for their Atlas service in 2021
还有一篇2007年的论文《Dynamo: Amazon’s Highly Available Key-value Store》,介绍了 Dynamo 的设计和实现。(没看过) 虽然名字有相似,而且都是 KV 数据库,但这是两个不同的东西。Dynamo 是个很难去运维的数据库。
SimpleDB
是 AWS 的第一个 Database-as-a-Service (DBaaS) 产品,但是它有一些限制:
- tables had a small capacity in terms of storage (10GB) and of request throughput
- unpredictable query and write latencies, which stemmed from the fact that all table attributes were indexed, and the index needed to be updated with every write.
DynamoDB 应运而生
Dynamo + SimpleDB = DynamoDB
DynamoDB 的设计目标是为了解决 SimpleDB 的限制,同时保留 Dynamo 的优点。
Architecture
- A DynamoDB table is a collection of items, and each item is a collection of attributes.
- Each item is uniquely identified by a primary key. The primary key schema contains
- a partition key or
- a partition and sort key (a composite primary key).
The partition key’s value is always used as an input to an internal hash function. The output from the hash function and the sort key value (if present) determines where the item will be stored.
hash(partition key) + sort key => where the item will be stored
- DynamoDB also supports secondary indexes to provide enhanced querying capability
Storage
The replication group uses Multi-Paxos for leader election and consensus. Any replica can trigger a round of the election. Once elected leader, a replica can maintain leadership as long as it periodically renews its leadership lease.
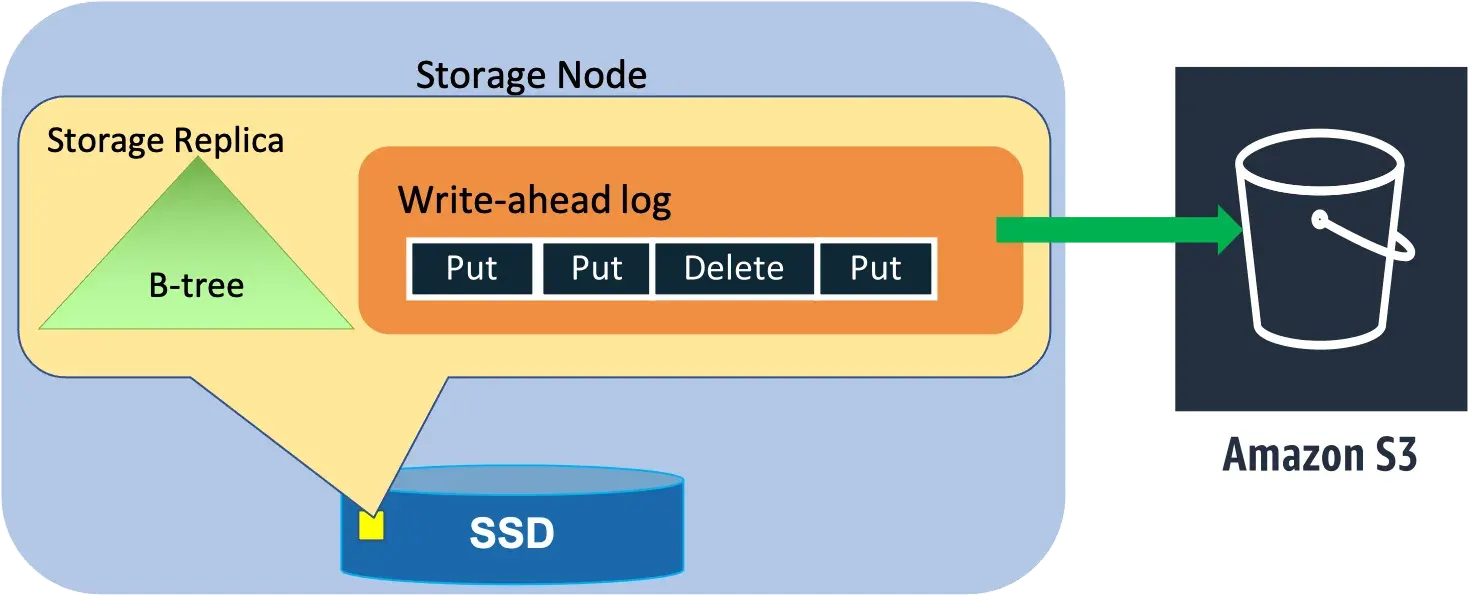
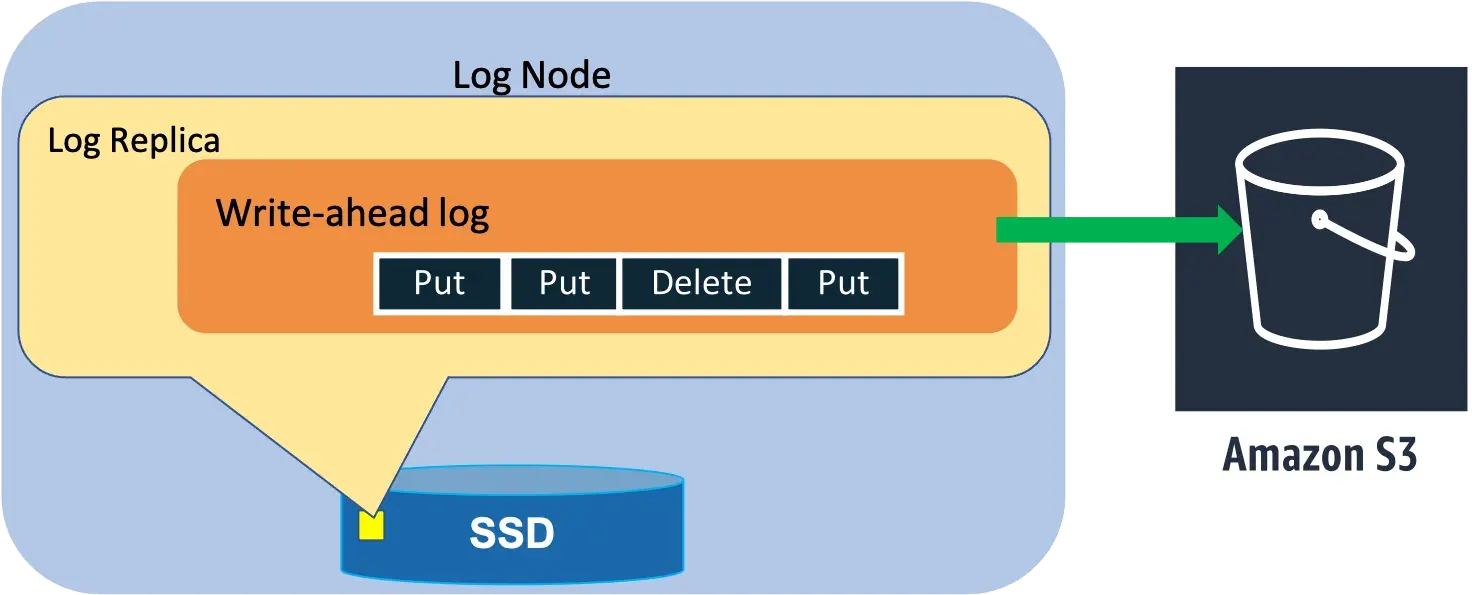
Storage Node and Log Node
- Write-ahead log
- B-tree stores the key-value data
- log replicas only persist recent write-ahead log.
Microservices
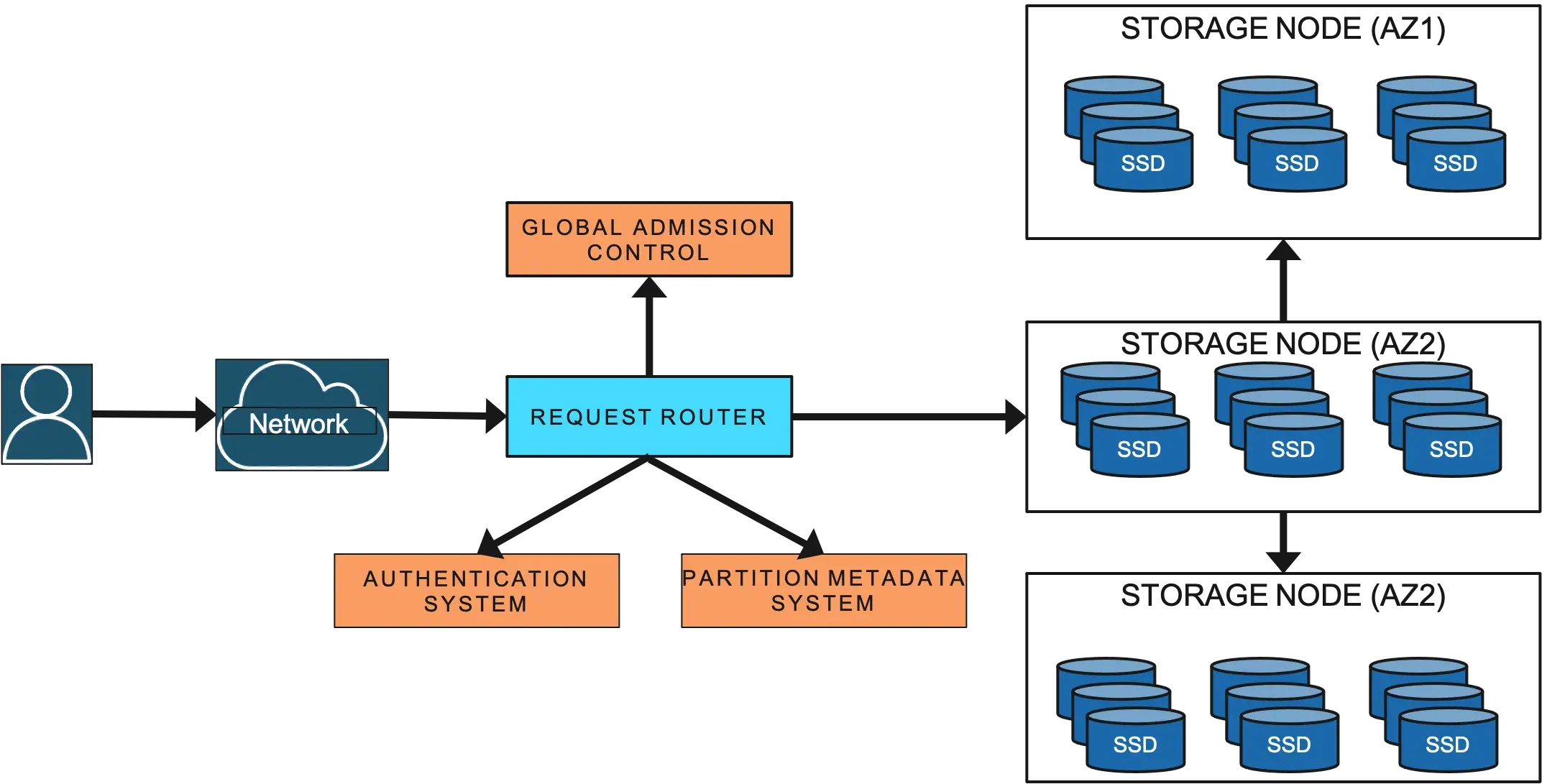
DynamoDB consists of tens of microservices.
- metadata service. stores
- routing information about the tables
- indexes
- replication groups for keys for a given table or index.
- request routing service - authorizing - authenticating - routing each request to the appropriate server.
For example, all read and update requests are routed to the storage nodes hosting the customer data. The request routers look up the routing information from the metadata service. All resource creation, update, and data definition requests are routed to the autoadmin service.
- storage nodes
- storing customer data on a fleet of storage nodes
- Each of the storage nodes hosts many replicas of different partitions.
- autoadmin service
- fleet health
- partition health
- scaling of tables
- execution of all control plane requests
- other services support features such as
- point-in-time restore
- on-demand backups
- update streams
- global admission control
- global tables
- global secondary indices
- transactions.
Provisioned to on-demand
If you can’t measure it, you can’t manage it - Peter Drucker
-
read capacity units (RCUs)
For items up to 4 KB in size, one RCU can perform one strongly consistent read request per second.
-
write capacity units (WCUs)
For items up to 1 KB in size, one WCU can perform one standard write request per second.
RCUs and WCUs collectively are called provisioned throughput.(pre-allocated capacity, 预配置)
Partition abstraction proved to be really valuable and continues to be central to the design of DynamoDB. 但是早期的版本将容量和性能紧密地耦合进了独立的 partition,带来了挑战。
DynamoDB 的接纳控制一开始是按照 provisioned throughput 来设计的,但实际情况通常是 non-uniform workloads.
数据的分布也很重要,一般来说请求并不会均匀分布到每一个 partition 的。会导致 hot portion
Since throughput was allocated statically and enforced at a partition level, these nonuniform workloads occasionally resulted in an application’s reads and writes being rejected, called throttling, even though the total provisioned throughput of the table was sufficient to meet its needs.
- DynamoDB uses admission control to ensure that storage nodes don’t become overloaded
- DynamoDB provisions the on-demand tables based on the consumed capacity by collecting the signal of reads and writes and instantly accommodates up to double the previous peak traffic on the table.
Others Points
- For higher durability, the write ahead logs are periodically archived to S3, an object store that is designed for 11 nines of durability.
- The process of healing a storage replica can take several minutes because the repair process involves copying the B-tree and write-ahead logs
- Adding a log replica takes only a few seconds because the system has to copy only the recent write-ahead logs from a healthy replica to the new replica without the B-tree.
- DynamoDB also continuously verifies data at rest. Our goal is to detect any silent data errors or bit rot in the system.
- AWS use formal methods extensively to ensure the correctness of the system.
- Backups or restores don’t affect performance or availability of the table as they are built using the write-ahead logs that are archived in S3.
- To achieve high availability, DynamoDB tables are distributed and replicated across multiple Availability Zones (AZ) in a Region.
Summary
本质上系统设计就是在做 tradeoff,有舍才有得。DynamoDB Serverless 很好用。 DynamoDB DAX 的本质就是签名加了一个 cache。